Coming Off of Celexa and Drink Alcohol Again
SSRI Citalopram to Treat Patients with Alcohol Use Disorder?
10% of all American adolescents and adults take an antidepressant
However, information technology is of import to understand the effectiveness of antidepressants for individuals with alcohol use disorder, because they are at college hazard for depressive symptoms and major depressive disorder.
WHAT PROBLEM DOES THIS STUDY Address?
Prior meta-analyses take found that the most popular form of antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), appear not to be effective in treating alcohol use or depressive symptoms among patients with alcohol use disorders (see hither and here).
However, some of the more recently developed SSRIs were not included in those studies. In the current report, Charney and colleagues tested in a randomized controlled trial whether the relatively new SSRI, citalopram, is effective for treating depression symptoms amidst individuals with alcohol use disorders.
HOW WAS THIS Study CONDUCTED?
- READ More ON STUDY METHODS
-
Authors compared the efficacy of citalopram (40mg per day) to placebo in 265 adult patients (n = 138 vs. 127, respectively) with booze use disorder who were receiving psychosocial habit treatment (ane individual and one group session weekly) across 12 weeks. Those with other substance utilize disorders equally well as those taking a psychotropic or anti-craving medication (e.m., naltrexone) were not able to participate. The groups were similar when commencement the study, autonomously from greater likelihood of requiring alcohol detoxification prior to entering the study in the citalopram condition (44 vs. 26%).
WHAT DID THIS STUDY FIND?
But 141 of 265 among the study sample remained in treatment across the entire 12 week study. (Though 63 of those who dropped out however provided post-treatment data).
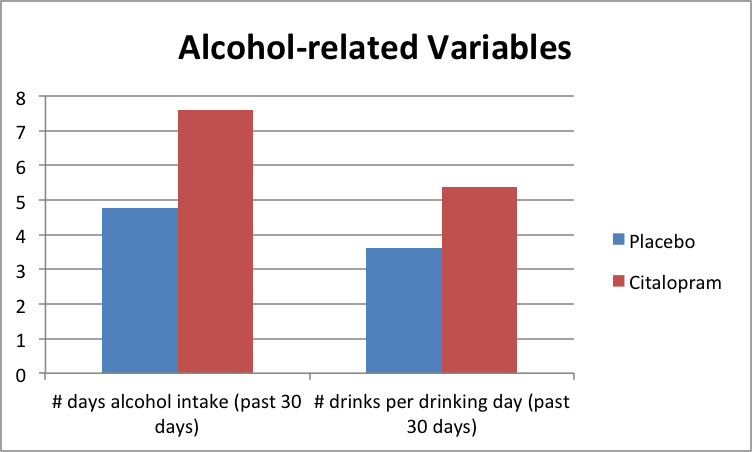
The primary findings were that patients in the citalopram condition did worse than placebo on drinking days and drinks per drinking 24-hour interval & spent more money on alcohol in the calendar month earlier the postal service-treatment follow-up interview ($248 vs. 148).
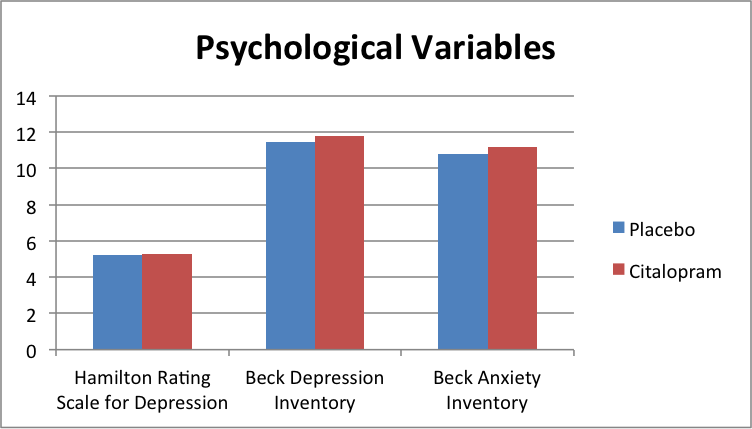
Like prior research on other SSRIs, the citalopram group did no better than the placebo on patients' self-reported and staff-rated measures of low and anxiety.
The placebo and citalopram groups were like on all other markers of severity, and although the citalopram group had a greater proportion of patients that needed detoxification prior to treatment, suggesting they may have been more severe to start, detoxification did not predict whether a patient had a complete vs. fractional/no response to treatment (100% reduction in drinking days and drinks per drinking day).
Although SSRIs may be a commonly prescribed medication, this written report adds to the body of literature suggesting:
a) they are not effective in helping reduce booze consumption among individuals with booze use disorder
b) they may non exist constructive in reducing depressive symptoms for this grouping of patients either.
WHY IS THIS Written report Important
Approximately twenty% of patients that seek treatment for alcohol use disorder have a co-occurring depressive disorder, and countless more nowadays with depressive symptoms that may be related to their alcohol utilize, or exercise non quite meet clinical thresholds.
It is important to determine what types of interventions, both pharmacological and psychosocial, can be nigh helpful.
In combination with many other studies on SSRIs in patients with alcohol utilize disorder (run into meta-analyses mentioned above), available evidence suggests SSRIs are unlikely to perform improve than a placebo medication, on boilerplate, for alcohol use and depressive symptoms in patients receiving handling for AUD.
Other antidepressants (e.one thousand., tricyclic) announced to exist more than effective medications in treating depressive symptoms in those with booze use disorder. As the study authors suggest, however, SSRIs still could exist considered once patients are abstemious for a menstruum of time (e.g., xxx days).
- LIMITATIONS
-
- Just virtually one-half of the patients completed the treatment suggesting medication adherence may not accept been adequate. However, because the trial'southward findings were generally consistent with other studies of SSRIs, it increases conviction that the effect was not due to poor medication adherence. More than importantly, poor medication adherence among those with AUD in research studies may reflect what happens in real-world clinical settings.
- As well, the study authors but were able to appraise 77% of participants at the end of treatment; however, they used a sophisticated statistical procedure chosen "multiple imputation" to fill in these missing data. The design of study findings were like whether authors used this multiple imputation procedure or analyzed only those who provided consummate data. Again, this raises confidence that the research was methodologically sound and the findings were an accurate reflection of how patients responded to citalopram.
BOTTOM LINE
- For individuals & families seeking recovery: An SSRI antidepressant like citalopram is unlikely to improve alcohol employ and may actually make it worse. In the instance of comorbidity, these antidepressants may not help improve your depression either. If y'all are interested in a medication to help with your depression, consider request your doctor about a non-SSRI antidepressant medications.
- For scientists: More than research on non-SSRI antidepressants for individuals with alcohol employ disorder and depressive symptoms or co-occurring depressive disorders is needed (see here for results of a recent airplane pilot report) to see if multimodal therapy tin raise remission rates.
- For policy makers: Consider funding research to develop and evaluate novel pharmacological treatments for patients with co-occurring alcohol utilise and depressive symptoms and disorders.
- For handling professionals and treatment systems: SSRIs are unlikely to be effective for patients with alcohol utilize disorder; other antidepressant medications may be considered in patients with clinically significant depression but volition need to weighed against other potential side effects and risk associated with taking these medications.
CITATIONS
Charney, D. A., Heath, L. M., Zikos, East., Palacios-Boix, J., & Gill, K. J. (2015). Poorer Drinking Outcomes with Citalopram Treatment for Alcohol Dependence: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. doi:ten.1111/acer.12802
wilsonusionswut53.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.recoveryanswers.org/research-post/ssri-citalopram-to-treat-patients-with-alcohol-use-disorder/
0 Response to "Coming Off of Celexa and Drink Alcohol Again"
Post a Comment